D-Coded Dictionary
Your essential glossary for diabetes, translating medical terms into everyday language.
ADA-recommended Goal
Fasting blood glucose: 80-130 mg/dL and postprandial (1-2 hours after meals) blood glucose: less than 180 mg/dL
ADA/EASD consensus
Joint guidelines by the ADA and EASD for managing diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes.
Adjunct glucose-lowering medications
Additional treatments used alongside insulin to lower blood sugar levels in diabetes.
Alloimmunity
An immune response occurring when the immune system reacts against antigens from the same species.
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2)
is a type of enzyme found in various tissues throughout the human body. Plays a role in the regulation of the blood pressure, fluid balance, and electrolyte homeostasis.
Artificial pancreas
An artificial pancreas, also known as a closed-loop system, is an advanced diabetes management technology designed to automate and optimize insulin delivery for people with diabetes. It integrates a continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) device, which measures blood sugar levels, with an insulin pump that delivers insulin into the body.
The artificial pancreas uses algorithms and sophisticated software to analyse the real-time glucose data from the CGM and adjust the insulin delivery accordingly. This automation aims to keep blood sugar levels within a target range, reducing the need for manual insulin adjustments by the individual.
By simulating the function of a healthy pancreas, the artificial pancreas can help people with diabetes achieve better blood sugar control, minimize the risk of hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar), and improve overall diabetes management. This technology represents a significant advancement in diabetes care, enhancing the quality of life and reducing the burden of constant diabetes monitoring and insulin administration.

An artificial pancreas is a device which keeps blood sugar levels within a target range, reducing the need for manual insulin adjustments by the individual.
Autoantibodies
Antibodies are immune system soldiers that lock onto and tag harmful invaders like germs so that other immune cells can destroy them.
Autoimmune diseases
Disorders in which the immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues and organs.
Auto Immune System
In autoimmunity, the immune system gets confused and mistakenly attacks the body’s own cells, leading to various diseases and health problems
Automated Insulin Delivery (AID)
Tools designed to automate and optimize insulin administration, including CGM, Insulin Pump, and an Algorithm.
β (beta) cells
Cells in the pancreas responsible for producing and secreting insulin.
Biomarkers
Biological markers that are measurable indicators of some biological state or condition.
Biosimilar
A medical product highly similar to an already approved original product, designed to have no clinical differences in safety, purity, and potency.
BMI
Body mass index: an individual’s weight in kg divided by their height in m².
Carbohydrates
One of the three main macronutrients found in food, alongside proteins and fats. Carbohydrates are an essential source of energy for the body, providing fuel for various bodily functions and activities.

Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)
Cell therapy
Medical treatment involving the use of living cells to replace or repair damaged or dysfunctional cells.
Clinical Trial
A clinical trial is a carefully planned medical study in which people participate to test new treatments or interventions, helping doctors and researchers determine their safety and effectiveness for specific conditions or diseases.
Comorbidity
Having two or more conditions at the same time.
Confidence Interval (CI)
Confidence Interval is a statistical concept used in inferential statistics to estimate a range of values within which a population.
Congenital Anomaly
Structural or functional abnormalities that occur during intrauterine life.
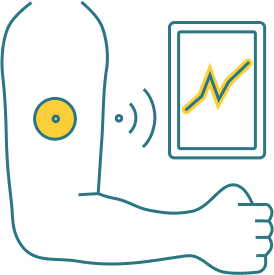
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
A system that measures glucose levels continuously throughout the day and night, providing real-time data to help people with diabetes manage their condition.
COVID 19
Coronavirus disease 2019 is a highly contagious, respiratory illness caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2.
Diabetes
Diabetes, often referred to as diabetes mellitus, is a chronic (long-lasting) medical condition characterized by high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. This occurs either because the pancreas does not produce enough insulin (a hormone that regulates blood sugar) or because the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin.

occurred by less production of insulin or body’s improper response to insulin.
Differentiated Islet Cell Therapy
The transplantation stem cells that are induced to differentiate into insulin-producing cells. These are transplanted into individuals with diabetes.
D.K.A.
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious and potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes, primarily affecting those with type 1 diabetes. It occurs when the body lacks insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels and the production of ketones, which can make the blood acidic.
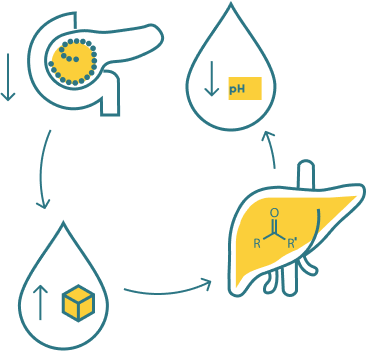
primarily affects those with type 1 diabetes.
Efficacy
Endogenous
Something that originates or arises from within a particular organism such as insulin.
Exogenous
Fat
Fat, also known as dietary fat or lipids, is one of the three main macronutrients found in food, alongside carbohydrates and proteins. It is a concentrated source of energy, providing more than twice the calories per gram compared to carbohydrates and proteins.

concentrated source of energy
Follow-on product
Products providing more treatment options, often at a lower cost, while maintaining or improving the outcomes of the original drug.
GEMELLI 1
A phase 3 clinical trial evaluating SAR341402, a biosimilar insulin aspart, compared to NovoLog in adults with type 1 diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes
A form of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy in some women. It usually resolves after childbirth, but women who have had gestational diabetes are at higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.

high risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
Diabetes treatments that mimic GLP-1, a hormone boosting insulin, suppressing glucagon, and aiding weight loss.

Glucose
A simple sugar and the body’s primary source of energy. It comes from the foods we eat and is carried by the bloodstream to cells for energy production.

Glucagon
It is a hormone which has a opposite function to the insulin, which increase the blood glucose level.

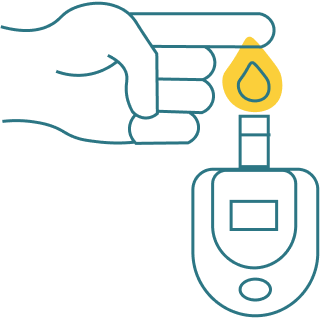
Glucometer
It is a gadget used to measure the blood glucose with just one drop of blood.
Glucose Tolerance Test
Is used to evaluate how effectively your body metabolizes sugar.
Placebo: is a substance or treatment that has no therapeutic effect on its own.
Glycemic Control
The way of managing the blood glucose level of diabetic patients at optimum level.
Glycemic Metrics
Various measurements used to assess blood glucose levels over time in individuals living with diabetes.
Glycemic Variability
Refers to fluctuations in blood sugar levels throughout the day, including both highs (hyperglycemia) and lows (hypoglycemia).
Gut flora
The complex community of microorganisms living in the digestive tracts of humans, playing roles in digestion and health.
HbA1c (Glycated Hemoglobin)
A blood test that measures the average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. It is used to monitor long-term diabetes control.
Hyperglycaemia
It is a condition where the blood glucose level goes high, more then 126 in case of fasting blood glucose and more than 200 normally. And during that situation the person need to take their medication to reduce the blood glucose to normal level.
Hypoglycaemia
It is a condition where the blood glucose level goes low, less than in 80 mg/dll . During that situation the person need to take Glucose or Hypo treats to increase the blood glucose to normal level.
Hepatic Portal Vein
A major blood vessel in the circulatory system that carries blood from abdominal organs to the liver.
Immunology
The branch of biomedical science that deals with the study of the immune system in all organisms.
Immunosuppressive Therapy
Refers to the medical treatment or use of drugs that suppress the activity of the immune system.
Insulin
A hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels by allowing glucose to enter cells for energy.
Insulin Aspart
A rapid-acting insulin analog used to control blood sugar levels in people with diabetes mellitus.

Insulin resistance
When an individual’s body does not respond properly to insulin, meaning they cannot efficiently take up glucose from the blood or store the glucose.
Insulin-producing cells (IPCs)
Specialized cells that synthesize and release insulin.
Intensive Insulin Therapy
Insulin delivered via multiple daily injections or pump therapy.
Islet Autoimmunity
An immune response directed against the insulin-producing beta cells in the islets of Langerhans.
Islet Cells:
Also known as islets of Langerhans, are clusters of cells found in the pancreas, play a crucial role in regulating blood glucose levels by producing hormones such as insulin and glucagon.

Ketones
ketones are chemicals produced by the body when it breaks down fat for energy in the absence of sufficient insulin.
Ketone Strips
Ketone strips are small, disposable test strips used to detect the presence of ketones in a person’s urine.
L.A.D.A
Latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA) is a type of diabetes that starts in adulthood and slowly gets worse over time. Like type 1 diabetes, LADA happens when the pancreas stops making insulin. That’s usually because an autoimmune process is damaging cells in the pancreas. But unlike type 1 diabetes, in LADA, the process happens slowly.

high risk of developing type 1 diabetes later in life.
MAG1C
A clinical trial investigating the efficacy and safety of metformin and liraglutide in glucose control in type 1 diabetes.
Monogenic diabetes
A rare form of diabetes caused by mutations in a single gene, unlike polygenic diabetes, which involves multiple genetic factors.
Myocardial Infarction
Pancreas
An organ located near the stomach that produces insulin and other digestive enzymes to help with food digestion and blood sugar regulation.
Placebo
A placebo is a harmless substance or treatment that has no therapeutic effect but is sometimes given to participants in a clinical trial to serve as a control, helping researchers assess the true effects of the experimental treatment.
Prediabetes
A condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed as Type 2 diabetes. It is a warning sign that indicates increased risk for developing diabetes if preventive measures are not taken.
Pre-eclampsia
A condition in pregnancy characterized by high blood pressure, sometimes with fluid retention and proteinuria.
Prevalence
A measure which indicates how many individuals have an illness at any one point in time.
P.R.I.S.M.A
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) is a widely recognized and used set of guidelines for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses. It aims to improve the transparency, and clarity of reporting.
Prognosis
It is the likely course of the condition, i.e., what might happen in the future pertaining to that condition. It’s like a weather forecast for your health.
Protein
Proteins are essential macronutrients found in food, composed of amino acids. They play crucial roles in the body, including building and repairing tissues, supporting immune function and many more functions .

PWT1D
“People with Type 1 Diabetes,” referring to individuals with Type 1 diabetes.
RBC
Hemoglobin-containing red blood cells that flow through our circulatory system and deliver oxygen to the body tissues.
Real world evidence
Data collected from everyday clinical practice and actual patient experiences outside of controlled clinical trials.
Retinopathy
Retinopathy is a medical condition that affects the eyes, specifically the retina. It is characterized by damage to the tiny blood vessels present in the retina that can eventually cause vision impairment.
SHEs
Severe hypoglycemic events associated with type 1 diabetes (T1D).
SAR341402
A biosimilar insulin aspart developed by Sanofi, similar in safety, efficacy, and quality to NovoLog, a rapid-acting insulin analog.
SARS-CoV-2
Severe Acute Respiratory syndrome Coronavirus 2 is a member of the coronavirus family and shares genetic similarities with other coronaviruses. It can cause respiratory illness that can range from mild, asymptomatic to severe cases requiring hospitalization.
SGLT2 inhibitors
Medications for diabetes that block glucose reabsorption in the kidneys, causing glucose excretion and lowering blood sugar.
SMBG
Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose, the process where individuals with diabetes regularly check their blood glucose levels using a glucose meter.
Stem cells differentiation
The process by which unspecialized stem cells develop into specialized cell types with distinct functions.
T cells
White blood cells that play a central role in the immune response. They originate in the bone marrow and mature in the thymus.
TEDDY study
“The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young,” a research project aimed at identifying environmental factors contributing to type 1 diabetes in genetically predisposed children.
Time in range (TIR)
A metric measuring the percentage of time a person’s blood sugar levels stay within a specified target range of 70 mg/dL to 180 mg/dL.
Transplantation Immunology
The immune response to transplanted organs, tissues, or cells from a donor to a recipient.
Trial Net
Is a network of clinical trials focused on identifying and monitoring individuals at risk of developing type 1 diabetes through screening for diabetes-related autoantibodies.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. As a result, the pancreas produces little to no insulin, leading to high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. People with type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy to regulate their blood sugar levels and manage the condition.
a chronic auto immune disorder that occurs when pancreas produces little to no insulin, leading to high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood.
Type 2 Diabetes
A metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin. This results in high blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes can often be managed through lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin therapy.

a metabolic disorder that occurs when insulin is resisted by body leading to high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood.
Vertex
Is a biopharmaceutical company that focuses on the discovery, development, and commercialization of innovative medicines for serious diseases.
Viral exposure
Contact or infection by viruses, which can replicate only inside living cells of an organism.