Understanding the article: “Significance of HbA1c Test in Diagnosis and Prognosis of Diabetic Patients”
Published Date:
9th June 2016
Published By:
Shariq I. Sherwani, Haseeb A. Khan, Aishah Ekhzaimy, Afshan Masood, Meena K. Sakharkar.
Approved By:
TO BE
Decoded By:
Dr. AnuHasini, MBBS, (MS ENT)
10 mins to read
- The T1D Takeaway
- This article is helpful for people with diabetes, be it type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes mellitus or LADA (latent autoimmune disease of adults) to encourage them to get HbA1c tested regularly for better glycemic control.
Word Wizard
- HbA1c serves as a vital diagnostic tool for various forms of diabetes, providing a comprehensive view of average blood glucose levels over 2-3 months.
- Elevated levels of HbA1c indicate higher risks of cardiovascular diseases and long-term diabetes-related complications.

Summary Snap
Shots
HbA1c is a reliable indicator for diagnosis, prognosis and management of diabetes.
Prime Insight
HbA1c is also known as glycated hemoglobin. The glucose in our blood binds with hemoglobin, resulting in the formation of HbA1c.
Imagine hemoglobin as a bus, and glucose in our blood as passengers who get on the bus. As time goes by, more and more glucose passengers hop on to the hemoglobin bus. So HbA1c is like counting all the glucose passengers on the bus to see how the sugar levels in our blood have been going around.
HbA1c is a reliable measure of long term glycemic control and correlates with risk of long term diabetes related complications.

HBA1C ≥ 6.5% CAN BE USED FOR DIAGNOSIS OF DIABETES AS AN ALTERNATIVE TO FASTING GLUCOSE . It also acts as an indicator of insulin resistance.
HbA1c can be measured by a blood test and provides us with information of average blood glucose levels of the individual for a period of 2-3 months, which is the normal lifespan of our red blood cells ( RBC).
Higher the blood glucose levels, more glucose binds to hemoglobin and greater is the value of HbA1c and vice versa.
HbA1c is directly proportional to blood glucose levels. Tests like fasting glucose tests give us the measurement of blood glucose at that particular moment of time, but does not give any information about the time course trend of glucose levels. However, HbA1c gives us a broader picture of 2-3 months.
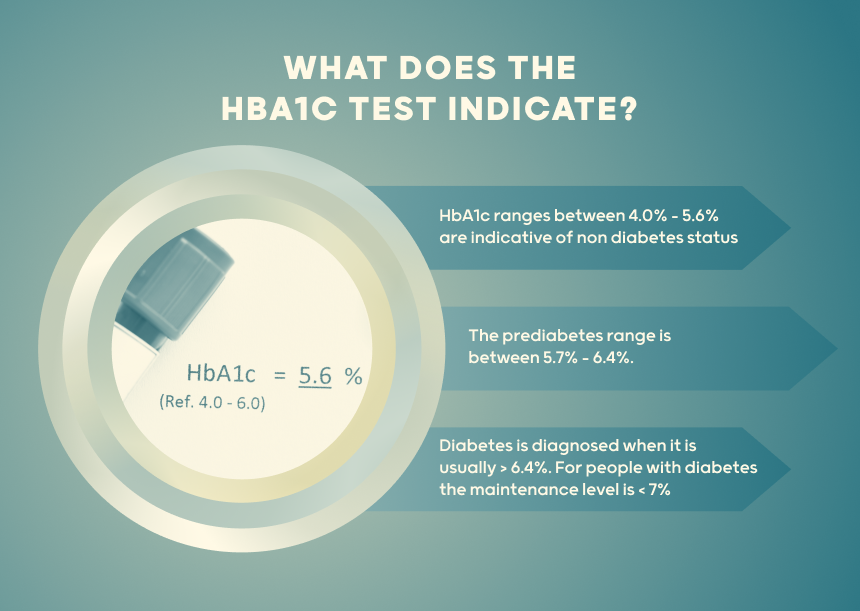
The prediabetes range is between 5.7% -- 6.4%.
Diabetes is diagnosed when HbA1c is usually 6.4% or higher.
Elevated levels of HbA1c point towards increased risk of cardiovascular disease as high HbA1c levels indicate high triglyceride levels in the body.Long term complications that are associated with diabetes are directly proportional to HbA1c, i.e a chronically higher value of HbA1c indicates higher risk of complications.
Advantage: HbA1c is a convenient test with high accuracy that does not require individuals to fast prior to the blood test.HbA1c ranges between 4.0% – 5.6% are indicative of non diabetes status.
- A Deeper Dive
- The Sources Voice
As the epidemic of diabetes continues to grow worldwide, including the HbA1c test as part of diagnostic and prognostic tools may lead to better care, management and successful clinical outcomes.
- Curiosities Clarified
As type 1 diabetes is insulin dependent, there is no substitute for daily monitoring of blood glucose levels as the amount of insulin to be taken before each meal is dictated by the blood glucose levels.
HbA1c should be periodically tested as advised by your physician. However it is suggested that a person living with Type 1 diabetes should get it tested four times a year and a person with type 2 diabetes should get their HbA1c tested at least twice a year, or more frequently if blood sugar levels exceed the recommended level of glycemic range, in order to plan further treatment.